Java Edition:Update Suppression
Update suppression prevents a block from receiving an update, this is done by throwing a Java exception before the game can process all of the updates, this is different from Update Skipping. This has many applications such as removing a block without updating the surrounding blocks, slicing nether portals, duplications, and item shadowing. This method is very powerful, and as such can be very dangerous, potentially making the world unplayable. Use update suppression with caution, and always create back ups of your world.
General Information
Update suppression heavily relies on the fact that all block updates will always be processed in a certain order, this order is West, East, Down, Up, North, and finally South. By chaining the updates from one side of a block into a device that throws a Java exception, the remaining sides can be skipped allowing the updates to never be processed. All sides except West may be suppressed, as the West side is the first in the update order and cannot be skipped.
The only type of update that can be safely chained into a suppressor are player updates as they are handled through a try catch block, which allows the exception to be safely handed. Before 1.8, update suppression must be done on a multiplayer server as the internal servers connection was not handled in a try catch block, this would cause any update suppression to crash the game which can corrupt or delete the level.dat file. The player must be careful when performing update suppression on block removals when playing on a laggy server or poor connection as the blocks removal might be scheduled for a later game tick, which results in the updates not being processed in a try catch block and crashing the game. A filter can be built for such events as showcased by FloppyDonkey.
Videos explaining the basics of update suppression, including subjects such as update order and safe usage:
Methods
Stack Overflow Exception
From the earliest versions[1][2] of Java Edition to 1.19 Deep Dark Experimental Snapshot 1, all block updates were handled with recursive methods. As more and more blocks are updated at once, the Java stack size will increase linearly with each block updated. If this stack exceeds the Java stack limit (the Java stack limit can vary from operating system, Java version, Java flags, hardware, etc.), a StackOverflowException will be thrown.
In 22w11a (a 1.19 snapshot), the recursive update stack was replaced with a queue[3][4], which avoids recursive function calls which patches this method.
This method can be accomplished by updating 2,000-3,000 blocks at once, though this can be lowered by changing the -Xss Java flag which determines the maximum size of the Java stack. The smallest this Java flag can be set to is -Xss160k, which reduces the blocks needed down to only a few hundred. One of the easiest methods is chaining signs or banners off of each other, attached to the block that is being suppressed. Although the signs and banners will drop once broken, they have to be placed back again making this a one-time use. Reusable suppressors typically use BUD powered rails, which can both chain the updates into the suppressor and do the actual suppressing.
Other reusable designs utilize unintentional recursive feedback loops.
Subtract Mode Comparator
When the instant tile ticks flag is enabled, comparators will instantly process their updates. When a subtract mode comparator's output loops into its input and receives a block update, the comparator will process itself continually until suppression.
BUD Powered Dispenser
When the instant tile ticks flag is enabled, dispensers will instantly process their updates. This can be abused by updating a BUD powered dispenser containing either a water or lava bucket. Dispensers do not set themselves as powered until after the liquid has been placed and the updates from that placement finish processing, so once the liquid is placed for the first time, it updates the dispenser which triggers another fluid placement until suppression occurs.
Trapdoor Dust Loop
An oversight in the 1.16 trapdoor code with redstone dust redirection allows for the creation of an update feedback loop. This method works from 20w18a (a 1.16 snapshot) to 1.19 Deep Dark Experimental Snapshot 1, but it can also be used as an update skipper until 1.20 Pre-release 1.
Some examples of reusable designs:
- Xcom6000 (rail based)
- FloppyDonkey (rail based)
- Sensei (rail based)
- LuisitoLapapa (trapdoor dust loop based)
Six Sided Pistons
Six Sided Pistons are pistons with a data value of 6, 7, 14, and 15 those with a data value of 6 and 14 are especially dangerous. These are created through block transmutation, this method works from Beta 1.7 until they are removed in 14w02a (1.8 Snapshot). Data value 6 pistons, when powered throw an ArrayOutOfBoundsException upon receiving an update, and data value 14 pistons will throw the exception regardless of whether it is powered or not.
Data value 6 pistons will sometimes check if they are receiving direct power upon being loaded from the disk, if the piston realizes that its hard powered when loaded, it can result in a crash loop until they are removed in 14w02a (1.8 Snapshot)[test]. This can be prevented by BUD powering the piston, this will allow the block updates to throw the exception, but will not potentially cause a crash loop.
Shulker Class Cast Exception
Using update suppression, tile entities can be swapped with other tile entities, this occurs because comparator updates are sent before the tile entity is removed. By suppressing the removal of a tile entity then placing another tile entity in its place, the tile entities can be swapped allowing for interesting combinations, such as a cactus with an inventory. However, the swapped tile entities may not play nice with each other.
When comparators receive an update, they attempt to update their power level depending on the tile entity they are facing away from. First, the comparator checks the block that it is facing away from then calls the getComparatorOutput from that blocks class. Shulker boxes specifically contain a direct cast of the block entity at the blocks location to the Inventory interface. Thus, if the tile entity fetched from the shulker box's position does not implement this interface, then a ClassCastException exception will be thrown.
There are two candidates that meet the requires of both sending comparator updates, and not implementing the Inventory interface: those are lecterns (with books) and Jukeboxes (playing a music disk). By suppressing their removal, and placing a shulker box at its location, the shulker box will then contain a tile entity that does not implement a Inventory interface. A comparator that attempts to read the shulker box's output will result in any update chain sent to the comparator throwing a ClassCastException exception. This suppressor can be disabled by powering a sollid block between the shulker box and the comparator as the comparator wi;; then read a signal strength of 15, thus preventing the comparator from attempting to read the shulker box's fill level.
This method can overcome the removal of recursive block update suppression as it can be created prior to when recursive suppression was patched, thus allowing one to maintain an easy to use suppressor past 1.19. This method works from 16w39a (1.11 Snapshot) to 23w33a (1.20.2 Snapshot).
Some examples of this method:
- Igna778 on utilizing OOM for 1.19+
- JKM115 on tile entity swap
- Captain_S0L0 tutorial for 1.11 to 1.12
- Captain_S0L0 tutorial for 1.13
- Captain_S0L0 tutorial for 1.14 to 1.16
- Captain_S0L0 tutorial for 1.17 to 1.20
Lever/Button & Shulker Box
In 17w18a (1.12 Snapshot), when a lever or button (wooden or stone) is updated when placed above a shulker, a NullPointerException exception will be thrown[5]. Toggling the lever or button will also throw the exception, but not in a useful manner, any updates chained into the lever or button will be suppressed.
Out Of Memory Exception
When traditional update suppression was removed in 22w11a (1.19 Snapshot), a new method was developed which throws the OutOfMemoryException exception. This method is tricky to use as it requires filling up the games RAM to a very specific amount to allow the upsizing of a HashSet which causes the game to be completely out of RAM, thus throwing the exception. This can be accomplished in two ways, either using synced block event queues, the entity UUID set.
Synced Block Event Queue
The synced block event queue is used to ensure some blocks have consistent update orders, mainly pistons. These scheduled events are usually ticked and discarded quickly, but by triggering pistons that are within border chunks, those events will not tick and will remain in the queue. If enough events are then scheduled to bring the list to the brink of upsizing, then a line of BUD powered rails are ran through unloaded chunks.
Once the line of BUD powered rails are updated, the high data chunks are loaded from the disk which fills the RAM to within a few megabytes of being full. Finally, at the end of the line of BUD powered rails, several floating comparators are updated as they handle updates through a necessary try catch block. Then the floating comparators update a handful of pistons to schedule more sync block events, causing the list to upsize, the RAM to fill, and the exception to be thrown.
Entity UUID Set
The entity UUID set is used to ensure that no loaded entities share a UUID, whenever an entity is loaded the game will add its UUID to this set. Entities can be loaded however one likes to fill the set, but its highly recommended to place these entities within border chunks as this will prevent them from being ticked by the game, greatly improving performance and allowing one to load millions of entities at once.
After bringing the entity UUID set to the brink of upsizing, a line of BUD powered rails ran through unloaded chunks which contain high amounts of data to nearly fill the games RAM. At the end of the line, a BUDded trapdoor is opened which allows a precise amount of support blocks (like signs) to be broken off resulting in item entities, bringing the set close of upsizing. This buffer is necessary to accommodate any normal entities that can load into the world normally before performing suppression. Lastly, BUDed TNT underneath the rails are updated, this allows the list to upsize with a catchable exception.
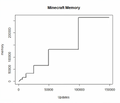
This method is particularly tricky as everyone's world will most likely need different amounts of data in the unloaded chunks to fill RAM to the proper amount. The table below provides the values where the sets upsize and how much RAM is necessary for each, or in other words, you need to have less than x bytes available when the upsize occurs at y entries to throw the exception.
| Upsize Values | ||
|---|---|---|
| Resize Value | RAM needed (<32 GB allocated) | RAM needed (>=32 GB allocated) |
| 1 | 16 bytes | 32 bytes |
| 2 | 32 bytes | 64 bytes |
| 4 | 64 bytes | 128 bytes |
| 7 | 128 bytes | 256 bytes |
| 13 | 256 bytes | 512 bytes |
| 25 | 512 bytes | 1 kilobyte |
| 49 | 1 kilobyte | 2 kilobytes |
| 97 | 2 kilobytes | 4 kilobytes |
| 193 | 4 kilobytes | 8 kilobytes |
| 385 | 8 kilobytes | 16 kilobytes |
| 769 | 16 kilobytes | 32 kilobytes |
| 1,537 | 32 kilobytes | 64 kilobytes |
| 3,073 | 64 kilobytes | 128 kilobytes |
| 6,145 | 128 kilobytes | 256 kilobytes |
| 12,289 | 256 kilobytes | 512 kilobytes |
| 24,577 | 512 kilobytes | 1 megabyte |
| 49,153 | 1 megabyte | 2 megabytes |
| 98,305 | 2 megabytes | 4 megabytes |
| 196,609 | 4 megabytes | 8 megabytes |
| 393,217 | 8 megabytes | 16 megabytes |
| 786,433 | 16 megabytes | 32 megabytes |
| 1,572,865 | 32 megabytes | 64 megabytes |
| 3,145,729 | 64 megabytes | 128 megabytes |
| 6,291,457 | 128 megabytes | 256 megabytes |
| 12,582,913 | 256 megabytes | 512 megabytes |
| 25,165,826 | 512 megabytes | 1 gigabyte |
| 50,331,651 | 1 gigabyte | 2 gigabytes |
| 100,663,301 | 2 gigabytes | 4 gigabytes |
| 201,326,601 | 4 gigabytes | 8 gigabytes |
| 402,653,201 | 8 gigabytes | 16 gigabytes |
The following resources give more information on this method:
This method works from 22w11a (1.19 Snapshot) until 24w20a (present).
23w13a_or_b's less_interaction_updates Vote
In the April Fools' version 23w13a_or_b the less_interaction_updates vote results in an effect that is similar to update suppression. Any block updates that would be produced from the player placing or breaking blocks are ignored while this vote is active. Other sources of updates (like redstone) still process there updates as they normally do. Do note that no actual errors are thrown, so this can not be used to swap tile entities, create shadow items, or duplicate items. However, if can still create many discontinued block configurations, including those on the West side of blocks which normal update suppressors are unable to do.
Uses
Alternative Discontinued Feature Methods
Update suppression can be used as an alternative to obtain discontinued block configurations. Any block with placement restrictions, such as support blocks or those only placeable on certain blocks, can have there restrictions bypassed by suppressing the removal of its supporter block and the placement of the invalid block. An example of this would be getting a Wither Rose on Nether Bricks as they are not normally able to be placed on Nether Bricks. This list includes, but is not limited to:
- Block Replacement Bypass
- Cactus Next to Invalid Block
- Concrete Powder Next to Any Waterlogged Block
- End Portal in the Nether
- Floating Gravity Block
- Floating Nether Sprout
- Floating Pointed Dripstone
- Flowing Lava on Top of Soul Soil and Adjacent to Blue Ice
- Full Block Chest
- Half Bed
- Half Door
- Half Double Chest
- Half Double Plant
- Invalid Block on End Portal Frame
- Invalid Flowing Liquids
- Invalid Nether Portal Configuration
- Invalid State Grass Block
- Moving Piston
- No Bubble Column on Soul Sand/Magma Block
- Occupied Bed
- Open Barrel
- Permanently Powered Lightning Rod
- Permanently Powered Target
- Plants Touching Liquids
- Short Lava Stream in the Nether
- Spawner with Chest Data
- Sugar Cane on Any Block
- Unconnected Chorus Plant
- Unconnected Dripleaf Stem
- Underwater Torch
- Vine on Invalid Block
Tile Entity Swap
Using update suppression, tile entities can be swapped with other tile entities, this occurs because comparator updates are sent before the tile entity is removed. By suppressing the removal of a tile entity then placing another tile entity in its place, the tile entities can be swapped allowing for interesting combinations, such as a cactus with an inventory. Only time entities that send comparator updates can be swapped with another tile entity, but they can be swapped with any other tile entity.
- Banner
- Barrel
- Beacon
- Beds
- Bee Nest
- Beehive
- Bell
- Blast Furnace
- Brewing Stand
- Cactus
- Campfires
- Chest
- Command Blocks
- Comparator
- Conduit
- Dispenser
- Dropper
- Enchanting Table
- End Gateway
- End Portal
- Ender Chest
- Furnace
- Hopper
- Jigsaw Block
- Jukebox
- Lectern
- Shulker Boxes
- Signs
- Skulls
- Smoker
- Spawner
- Structure Block
- Trapped Chest
Examples of the end gateway and end portal tile entity setups:
Duplication
When a player places a block, all updates are processed before the block is removed from the player's inventory. If an exception is thrown while the game is processing updates, the code to remove the item from the player's inventory will not be called, this allows for blocks to be duplicated. However, this does not preserve block inventories, so placing blocks which are holding items such as a shulker box, will not preserve the blocks inventory leaving an empty block.
When a player places an item into an item frame, if a floating comparator is updated with an item frame and the update is suppressed, the code to remove the item from the player's inventory is skipped. This allows for items to be duplicated. This does preserve block inventories, so inserting blocks which are holding items such as a shulker box into the item frame, will preserve the blocks inventory duplicating its contents as well.
Item Shadowing
From 1.8 to 1.19 Deep Dark Experimental Snapshot 1, update suppression could be utilized to duplicate references of a single ItemStack, allowing for an item to be in two places at once. This could be used for many things, some examples include creating automatically repairing tools by having a player with an instance of a tool with Mending AFK at an XP farm, or automatically siphoning resources to your base as you mine them. These duplicated references also allow for item duplication in a number of ways.
Item Shadowing 1.8-1.11
From 1.8 to 1.11, the only inventory manipulation method which preserved the ItemStack reference was the direct swapping of an item with another item that it cannot stack with in the cursor. To shadow items create the below setup, with the rail line pointing to your suppressor of choice. Place a sacrifice item into the container and another into your inventory, then suppress the removal of the block below the comparator to leave it floating. Open the container and take out the stack which you want to shadow, click once on the sacrifice item in the container, click once on the item in your inventory, click on an empty slot, then close and re-open the container.
Item Shadowing 1.12-1.17
From 1.12 to 1.17, the slotClick was rewritten and allowed for number key swapping to preserve ItemStack references, this is used to split the references. To shadow items create one of the below setups, with the rail line pointing to your suppressor of choice. Either suppress the removal of the block below the comparator, or open the trapdoor below the comparator to leave it floating. Open the container and number key the stack you wish to shadow into the container, then close and re-open the container.
Item Shadowing 1.18
From 1.18 to {{version | Deep Dark Experimental Snapshot 1 | 1.19 Deep Dark Experimental Snapshot 1}[test], number key swapping was patched to prevent item shadowing, so the direct swapping on an item with another item it cannot stack with must be used to split the references. The shadow items create the below setup, with the rail line pointing to your suppressor of choice. Place a sacrifice item into the container and another into your inventory, then open the trapdoor below the comparator to leave it floating. Open the trapdoor below the comparator to leave it floating. Open the container and take out the stack which you want to shadow, click once on the sacrifice item in the container, click once on the item in your inventory, click on an empty slot, then close and re-open the container.
Examples and resource on creating, utilizing, and duplicating with item shadowing:
- Captain_S0L0 showcasing the 1.12 method.
- Captain_S0L0 showcasing the 1.12 method.
- Captain_S0L0 showcasing the 1.18 method.
- Fallen Breath's explanation (lots of information on handling shadowed items)
- FX - PR0CESS (practical utilization of shadowed items with redstone)
Waterlogging Falling Blocks
Update suppression can can be used on falling blocks to obtain that falling block with its waterlogged state. When falling blocks land in water, if they are waterloggable, the falling block will set itself to waterlogged for a brief moment as it places itself into the world. If the updates from that placement are suppressed then the falling block may be recovered, but as its waterlogged variant. This can be performed on falling blocks obtained from any falling block in 1.12.
Resources on creating waterlogged falling blocks:
Population Suppression
Update suppression can be applied to world generation, this can be used to toggle hidden and extremely powerful game flags which allows the player to access many unique mechanics and broken exploits
See also
- Update Skipping
- Chunk Savestating
- Chunk Regeneration
- Parallel Asynchronous Threads
- Population Suppression
- Minecraft Wiki:
Notes
- ↑ Prior to 1.17, comparators did not have complete update code for jukeboxes, so workarounds need to be used to allow jukeboxes to be tile entity swapped. From 1.5 to 1.12.2, the player must suppress the insertion of a music disk into the jukebox, this prevents the tile entities cashed block state from being cleared which allows another check when breaking the jukebox to produce comparator updates. From 1.13 to 1.16.5, the player must directly replace the jukebox with a non-air block to allow comparator updates to occur when breaking, this can only be down with portal blocks. Nether portal placement can only be suppressed on a multiplayer connection, crashing if attempted with a singleplayer connection and deleting the tile entity, using end portals can only be used to swap a jukebox into an end portal as end portals cannot be removed in a way that preserves the jukebox tile entity.
- ↑ Prior to 1.17, comparators did not have complete update code for lecterns, so workarounds need to be used to allow lecterns to be tile entity swapped. The player must place a book with 2 or more pages into the lectern then suppress the block updates from the block location below the lectern which receives updates upon the lectern switching to its powered state when turning the books pages. This will produce a permanently powered lectern which allows for updates to be provided again to the block location below the lectern upon breaking the lectern in the correct phase of block breaking to preserve the lectern tile entity.